.png)
Mosaic Biosciences:
Internal Program
Mosaic harnesses vast internal expertise in yeast display technology for antibody discovery and optimization.
Expertise
Utilized
Protein engineering, yeast display, protein expression and purification, SPR,
Solving Drug Discovery Challenges: Optimizing a targeted bispecific antibody to improve expression and binding
P95
Improved binding potency
50X
increase in antibody expression
High
monomericity
Overview
The two most common general methods for discovering monoclonal antibodies are immunization of animals and molecular evolution, such as phage or yeast display. While there are limitations to both methodologies, the use of display technologies has many important advantages to the discovery of therapeutic drugs.
First, antibody libraries can be created “synthetically” thereby allowing for diversity that is not limited by in vivo biological systems. Also, display technologies are less dependent on target homology as there is no immune system to protect against self-reativity. Next, binding can be enhanced or removed for specific regions with biochemical positive and negative selection. Finally, yeast display technology allows for the selection of characteristics that are important for drug development such as increased expression, Tm, and stability. Yeast display thus increases the probability that an antibody will have good biophysical and manufacturing properties necessary for an antibody drug.
Herein, we provide examples of antibody optimizations using yeast display that provide advantages beyond binding potency to the human target.
Method Highlights
Molecular Evolution with Yeast Display:Antibody optimization libraries were created by either error-prone PCR techniques for the light and heavy chains (p95 and 1 TM) or synthetic design of CDRs and humanization framework toggle-points (soluble target).

Protein Generation:Protein production utilized expi293 cells with protein A purification.
Binding Assays:SPR/BLI-based binding was done by affixing antibodies to the surface with an anti-human antibody and flowing over the targets, using either an Octet or Biocore
Results
P95 cancer target with an antibody in need of optimization
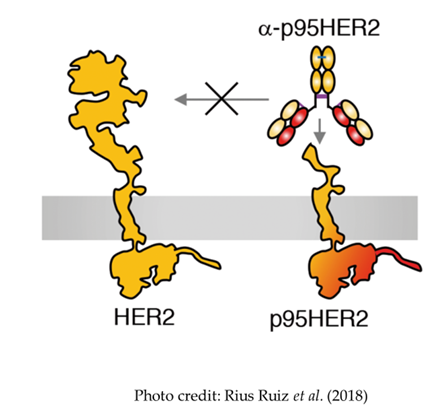
- A truncated form of HER2, the P95 variant, is specifically overexpressed on cancer cells and represents an interesting target for cancer therapies, particularly T cell engaging bispecifics
- Current anti-P95 antibody is poorly expressed and has low potency
- We used error-prone PCR on the heavy chain to improve expression and affinity
Yeast display improved binding potency of p95 antibody

- After 4 rounds of affinity maturation from 500 nM to 50 pM, variants were reformatted into IgG and expressed in mammalian cells
- KD was measured on Biacore by affixing antibodies to surface with an anti-human antibody and flowing ligand, ultimately showing a five-fold improvement in KD for discovered variants
Anti-p95 expression levels were increased by 50-fold in the higher potency variants and SEC shows high monomericity

Protein A titers in cell culture supernatants (CCS) were measured by Octet for parental molecule and discovered variants, with a 50-fold improvement in expression for multiple variants, which all look pure by GFC
Conclusion:
Using yeast surface display, a poorly expressed p95-binding mAb was optimized for nearly an order of magnitude improvement in potency and nearly two orders of magnitude increased expression.
These characteristics provide advantages for antibody drug devlopment beyond binding potency to the human target.
Furfine et. al. (2023) "Yeast Display Antibody Platform Optimizes for Multiple Characteristics in Parallel" PepTalk Conference