
Catalyst
Biosciences
Catalyst is a biopharmaceutical company focused on protease therapeutics targeting the coagulation system
Expertise
Utilized
Protein engineering, protein expression and purification, functional cell based assays, PK/PD sample analysis
How Catalyst Biosciences partnered with Mosaic to develop a long-acting C3 inactivator for GA and dAMD
PEG CB-2782
No change
in enzyme activity after protease modification
55%
increase in ocular half-life
99%
elimation of C3 after 28 days
Overview
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the leading cause of irreversible blindness. Progression of AMD to geographic atrophy significantly threatens vision, leading to progressive and irreversible loss of visual function. There are currently no approved therapeutics commercially available for GA patients.
Mutations in numerous genes in the complement cascade result in increased risk of AMD such as Factor H, Factor I, C9, and C3. There is substantial interest in blocking complement activation in the eye by inhibiting C3, with clinical data from a Phase 2 C3 inhibitor (APL-2) significantly inhibiting the progression of GA, albeit with limitations in feasibility. Mosaic and Catalyst engineered a PEGylated long-acting protease, which eliminates C3 catalytically, improving upon efficacy and patient burden.
Method Highlights
Protein Engineering: CB 2782 was engineered in E. coli from a human serine protease to degrade human C3 into inactive fragments. A single unpaired cysteine was added to CB 2782 and modified with a 40 kDa linear PEG by maleimide coupling.
Functional Assays: Enzymatic activity and specificity of CB 2782 and PEG-CB 2782 were evaluated with peptide hydrolysis assays and human C3 cleavage. Inhibition of complement activation was evaluated in standard sheep red blood cell hemolysis assays.
PK/PD Studies: Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics (C3 level) were evaluated in rabbit and African green monkey primate models. Vitreous humor was sampled at multiple time points up to sacrifice at 1, 14, and 28 days. Drug concentrations were determined by enzyme activity, while C3 levels were determined by ELISA.
Results
PEGylation of CB 2782 extends the ocular half-life in rabbits and has similar pharmacokinetics to aflibercept
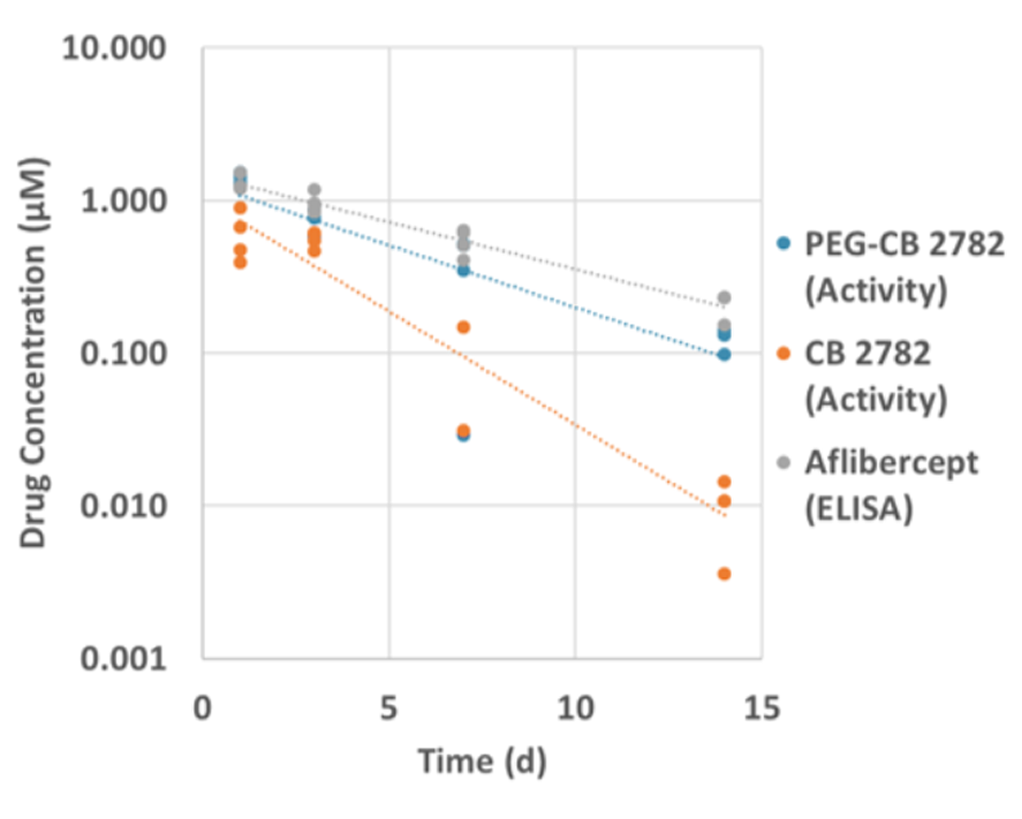
The increased size of PEG-CB 2782 resulted in enhanced ocular half life in rabbits (3.9 vs 1.9 days for the unmodified CB 2782) and in non-human primates (3.7 vs. 1.7 days).
Intravitreal PEG-CB 2782 eliminates at least 99% of vitreous humor complement C3 for at least 28 days in NHP model
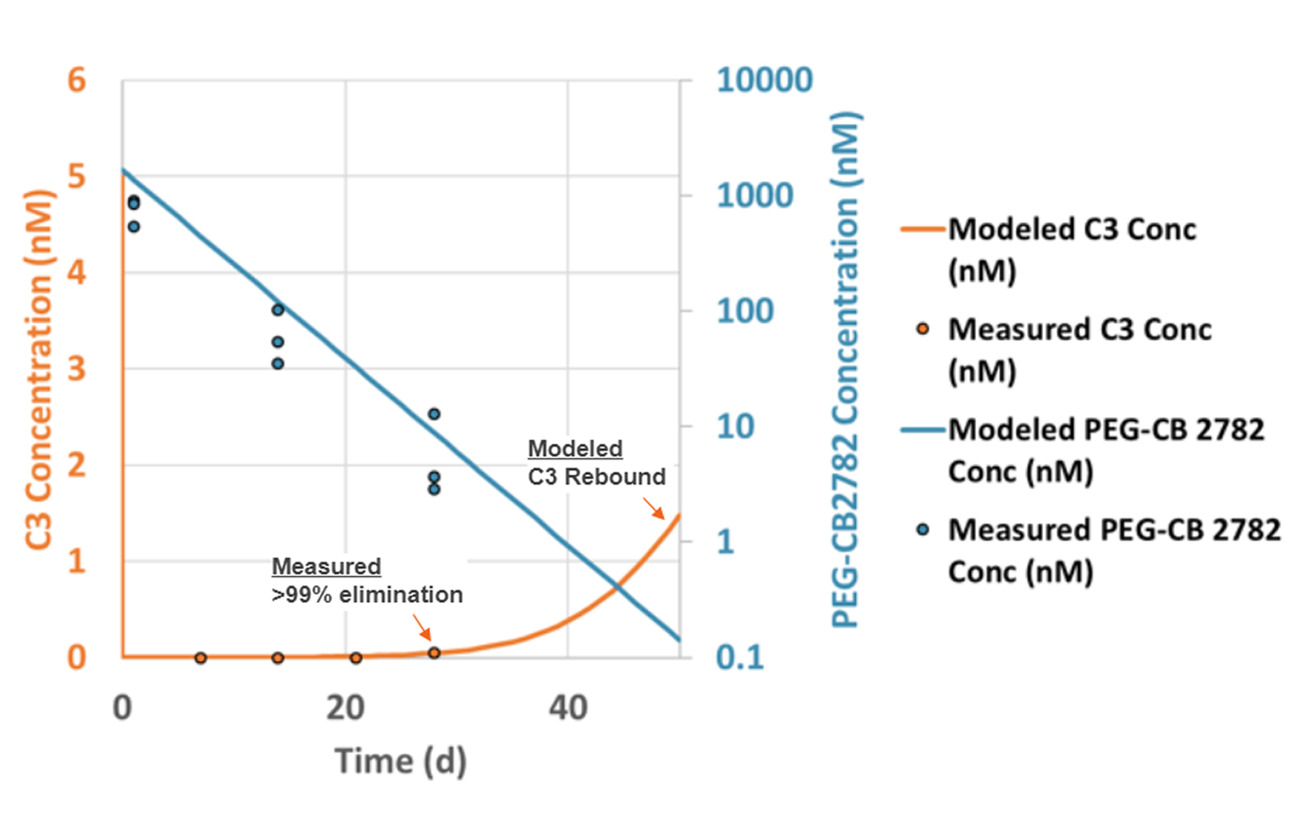
| Parameter | PEG-CB 2782 |
|---|---|
| t1/2 terminal (d) | 3.7 |
| Mean residence time (d) | 3.37 |
Non-human primate PEG-CB 2782 half-life measured at 3.7 days scales to 8.5 days in humans
8.5 day half-life and 2 mg dose suggests PEG-CB 2782 intravitreal administration three or four times a year in humans
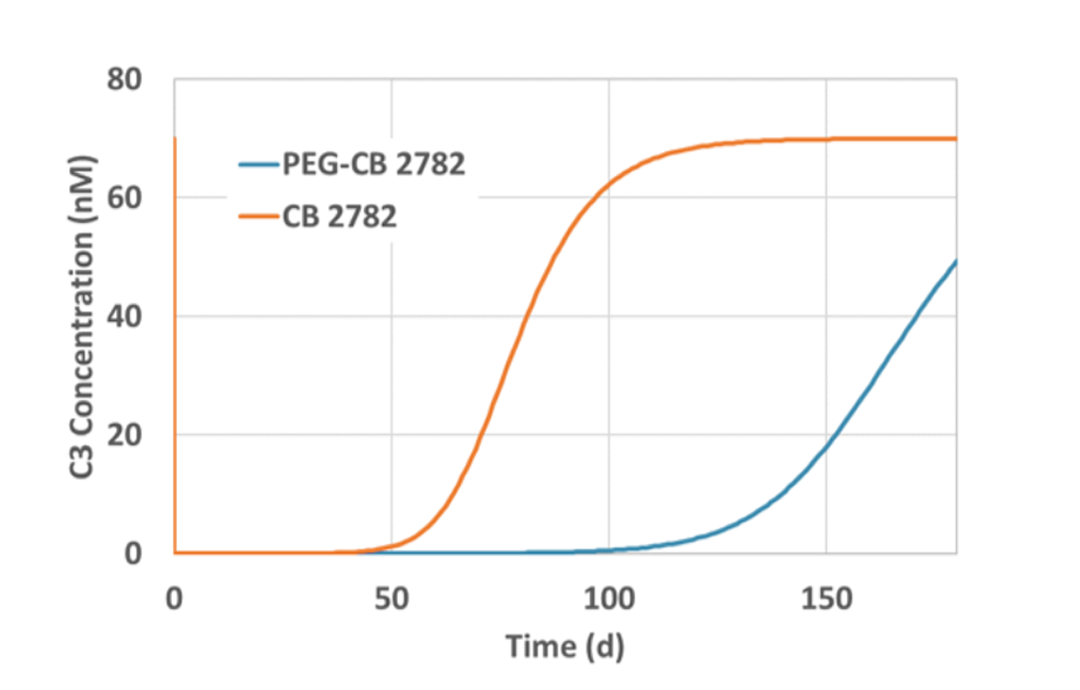
Conclusion: PEG-CB 2782 has the potential for anti-C3 best-in-class efficacy and convenience in geographic atrophy dry AMD with anticipated intravitreal dosing three or four times a year in humans
Furfine et. al. (2019) "PEG-CB2782: A Complement Factor C3-Inactivating Protease and Potential Long-Acting Treatment for Dry AMD" Annual Meeting of the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology